Red, itchy and irritated eyes are not always caused by an inflammation of the eye; instead, inflammation of the eyelids may be the culprit. Our eyelids are constantly exposed to dust, bacteria, and pollution which can produce swelling or infection. These delicate structures are also susceptible to hormonal changes, side effects of medications and a poor diet. Whatever the cause, chronic or acute inflammation of the eyelids affects the integrity of the eye and may result in uncomfortable symptoms. Some patients may experience only mild irritation that can be easily managed with topical medications while others may require surgery to prevent damage to the eye.
What causes eyelid inflammation?
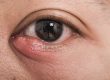
The medical term for an eyelid that is red and swollen is blepharitis. This is a very general term and it can be used to describe inflammation from any source. An eyelid may become inflamed due to an allergic reaction, as in eyelid dermatitis, or due to a medical condition such as rosacea and psoriasis. The latter are common diseases that may result in scarring of the cornea and irreversible visual loss if left untreated. A consultation with a dermatologist is important in these cases.
The overgrowth of bacteria on the base of the eyelashes is one of the main causes of eyelid inflammation in patients with blepharitis. This is very common in patients with a condition known as seborrheic blepharitis. Most of these patients also have oily skin and excessive dandruff. The bacteria living on the base of the eyelashes absorb this dandruff and secrete toxic substances that produce inflammation of the surface of the eye.
A poor diet consisting of mainly refined sugars and unhealthy fats can worsen eyelid inflammation in patients with a genetic predisposition to develop blepharitis. In addition, stress hormones may also trigger unwanted symptoms in patients. A parasite known as demodex is yet another cause of chronic blepharitis and should be identified and treated accordingly.
What are the symptoms of blepharitis and how can we treat them?
The main symptoms of this condition are red and itchy eyes, a constant burning sensation, crusting, eyelid swelling, and loss of eyelashes in severe cases. Most people experience repeated episodes of inflammation separated by asymptomatic periods. Both eyes are usually affected at the same time, although one eye may experience more discomfort.
Although blepharitis is a chronic condition, the symptoms of the disease can be managed. Medicated eyelid scrubs are a good option to reduce the bacterial load on the eyelashes and to reduce flakiness. Antibiotic ophthalmic ointments or drops can also help to decrease eyelid inflammation and eye redness. Dry eye clinics specialize in the treatment of these symptoms by using sophisticated technology to restore the health of the eyelids.
If the condition is not treated adequately, painful styes may form on the eyelids. These can be treated with warm compresses and antibiotic ointment. If styes form frequently, the patient should begin an eyelid cleansing routine and oral antibiotics.
Rosacea and psoriasis should be treated in conjunction with a dermatologist. Topical drops and an eyelid cleansing routine work well to keep the inflammation in check. Patients with severe rosacea require aggressive therapy with oral and topical antibiotics, and close observation by an ophthalmologist to prevent significant corneal damage.
Don’t let blepharitis affect your quality of life
Although blepharitis is hard to treat, there is no reason to allow it to affect your quality of life. A multidisciplinary approach, in which an ophthalmologist and dermatologist work together to create a treatment plan will result in the best outcome. With the right therapy, you will live symptom-free.










 |
|