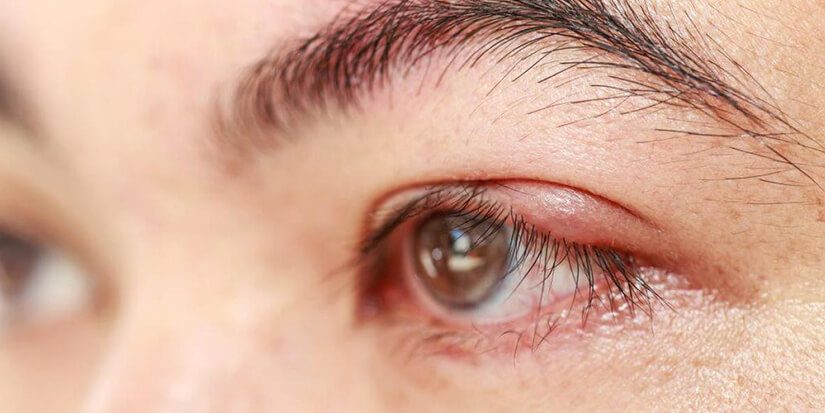
Chalazion are common non-infectious inflammatory lumps that may appear on the upper or lower eyelids. In many cases, they originate from an hordeolum, also known as a stye, which is a small, painful swelling of the eyelid margin caused by a bacterial infection. Oil-producing glands called Meibomian glands are the target of these infections. After the gland has been cleared of infection, either with medical treatment or the bodies’ own defense mechanisms, it may become clogged up and a chalazion forms.
The management of chalazion may be conservative or it may require surgery. The conservative approach consists of warm compresses applied to the swollen area, eyelid massage, and topical ophthalmic drops. Unfortunately, this approach is seldom effective in eradicating the lump.
Surgical excision of the chalazion is the most effective approach. It is an outpatient procedure done under local anesthesia. The operation takes about 10 minutes and it is only mildly uncomfortable. After the chalazion is removed, the operated eye is patched, and the patient is discharged. Topical antibiotic/anti-inflammatory drops are used in the operated eye for one week.










 |
|